Table Of Content :
- Google operator syntax
- Google’s advanced operators
- Intitle and allintitle
- Intext and Allinetext
- Inurl and allinurl
- Filetype
- LinkINanchor
- Cache
- Numrange
- Date range
- Info
- Related
- Author
- Group
- Insubject
- Msgid
- Stocks
- Define
- Phonebook
- Site
- Colliding Operators and bad Search-Fu
Google Operator Syntax
Advanced operators are additions to a query designed to narrow down the search results. Although they re relatively easy to use, they have a fairly rigid syntax that must be followed.
The basic syntax of an advanced operator is operator:search_term. When using advanced operators, keep in mind the following:
■ There is no space between the operator, the colon, and the search term. Violating this syntax can produce undesired results and will keep Google from understanding what it is you’re trying to do. In most cases, Google will treat a syntactically bad advanced operator as just another search term. For example, providing the advanced operator intitle without a following colon and search term will cause Google to return pages that contain the word intitle.
■ The search term portion of an operator search follows the syntax discussed in the previous chapter. For example, a search term can be a single word or a phrase sur- rounded by quotes. If you use a phrase, just make sure there are no spaces between the operator, the colon, and the first quote of the phrase.
■ Boolean operators and special characters (such as OR and +) can still be applied to advanced operator queries, but be sure they don’t get in the way of the separating colon.
■ Advanced operators can be combined in a single query as long as you honor both the basic Google query syntax as well as the advanced operator syntax. Some advanced operators combine better than others, and some simply cannot be combined. We will take a look at these limitations later in this chapter.
■ The ALL operators (the operators beginning with the word ALL) are oddballs. They are generally used once per query and cannot be mixed with other operators. Examples of valid queries that use advanced operators include these:
■ intitle:Google This query will return pages that have the word Google in their title.
■ intitle: “index of” This query will return pages that have the phrase index of in their title. Remember from the previous chapter that this query could also be given as intitle:index.of, since the period serves as any character.This technique also makes it easy to supply a phrase without having to type the spaces and the quotation marks around the phrase.
■ intitle: “index of” private This query will return pages that have the phrase index of in their title and also have the word private anywhere in the page, including in the URL, the title, the text, and so on. Notice that intitle only applies to the phrase index of and not the word private, since the first unquoted space follows the phrase index of. Google interprets that space as the end of your advanced operator search term and continues processing the rest of the query.
■ intitle: “index of” “backup files” This query will return pages that have the phrase index of in their title and the phrase backup files anywhere in the page, including the URL, the title, the text, and so on. Again, notice that intitle only applies to the phrase index of.
Google’s Advanced Operators
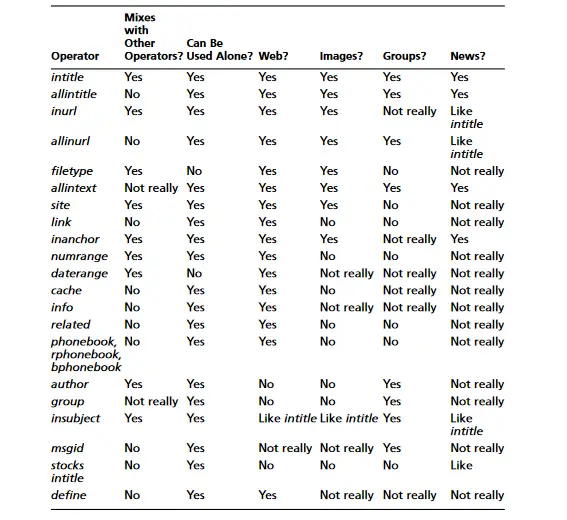
Google’s advanced operators are very versatile, but not all operators can be used everywhere,
1. Intitle and Allintitle
Search Within the Title of a Page
intitle
Function: restricts results to sites within the specified domain
Examples : site:google.com fox will find all sites containing the word fox, located within the *.google.com domain
Allintitle
Function: restricts results to documents whose title contains all the specified phrases
Examples: allintitle:foxfire will find all sites with the words fox and fire in the title, so it’s equivalent to intitle:fox and intitle:fire
2. Intext and Allintext
Locate a String Within the Text of a Page
intext
Function: Find text on pages
Examples: Usage: intext:Goodmorning ladies and gentlemen
Result: will get sites with most those words in a phrase
allintext
Function: Finds all text on page
Examples: Usage: intext:Goodmorning ladies and gentlemen
Result:exact copy of text
3. Inurl and Allinurl
Finding Text in a URL
inurl
Function: restricts results to sites whose URL contains the specified phrase
Examples: inurl:foxfire will find all sites containing the word fire in the text and fox in the URL
allinurl
Function: restricts results to sites whose URL contains all the specified phrases
Examples: allinurl:foxfire will find all sites with the words fox and fire in the URL, so it’s equivalent to inurl:fox inurl:fire
5. Filetype
Narrow Search to Specific Sites
Function: restricts results to documents of the specified type
Examples: filetype:pdf fire will return PDFs containing the word fire, while filetype:xls fox will return Excel spreadsheets with the word fox
6. Link
Search for Links to a Page
Function: restricts results to sites containing links to the specified location
Examples: link:www.google.com will return documents containing one or more links to www.google.com
7. Inanchor
Locate Text Within Link Text
Function: restricts results to sites containing links with the specified phrase in their descriptions
Examples: inanchor:fire will return documents with links whose description contains the word fire (that’s the actual link text, not the URL indicated by the link)
8. Cache
Show the Cached Version of a Page
Function: Cached version of site on google
Examples: cache:site.com
9. Numrange
Search for a Number
Function: restricts results to documents containing a number from the specified range
Examples: numrange:1–100 fire will return sites containing a number from 1 to 100 and the word fire. The same result can be achieved with 1..100 fire Result:exact copy of text
10. Daterange
Search for Pages published within a certain date
Function: Search for Pages Published Within a Certain Date Range
Examples: daterange:2452164-2452164 “osama bin laden”
11. Info
Show Google’s Summary Information
Function: Show Google’s Summary Information about a particular thing
Examples : info: linux
12. Related
Show Related Sites
Function: The related operator displays sites that Google has determined are related to a site,
Examples:related:linux
13. Author
Search Groups for an Author of a Newsgroup Post
Function: The author operator will allow you to search for the author of a newsgroup post
Examples: author:[email protected]
14. Group
Search Group Titles
Function: This operator allows you to search the title of Google Groups posts for search terms
Examples: group:*.forsale
15. Insubject
Search Google Groups Subject Lines
Function: The insubject operator is effectively the same as the intitle search and returns the same results.
Examples: insubject:dragon
16. Msgid
Locate a Group Post by Message ID
Function: Locate a Group Post by Message ID
Examples: [email protected]
17. Stocks
Search for Stock Information
Function: The stocks operator allows you to search for stock market information about a particular company.
Examples: stock:wipro
18. Define
Show the Definition of a Term
Function: The phonebook operator searches for business and residential phone listings
Examples: phonebook:john darling ny
19. Phonebook
Search Phone Listing
Function: The define operator returns definitions for a search term. Fairly simple, and very straightfor- ward, arguments to this operator may be a word or phrase.
Examples: define:hacking
20. site
Narrow Search to Specific Sites
Function: restricts results to sites within the specified domain
Examples: site:google.com fox will find all sites containing the word fox, located within the *.google.com domain
Colliding Operators and Bad Search-Fu
As you start using advanced operators, you’ll realize that some combinations work better than others for finding what you’re looking for. Just as quickly, you’ll begin to realize that some operators just don’t mix well at all.